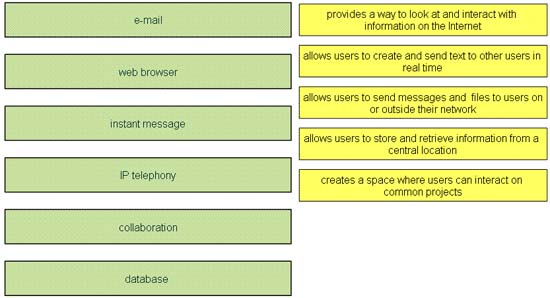
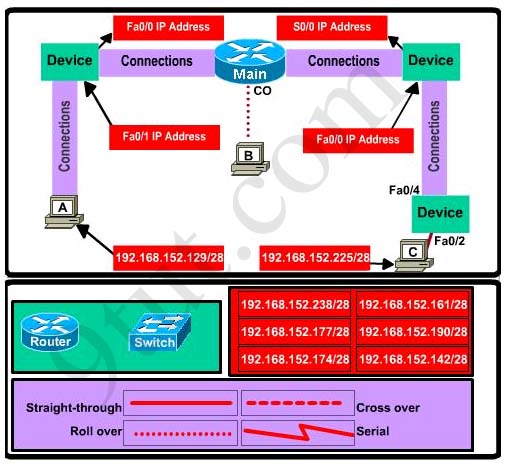
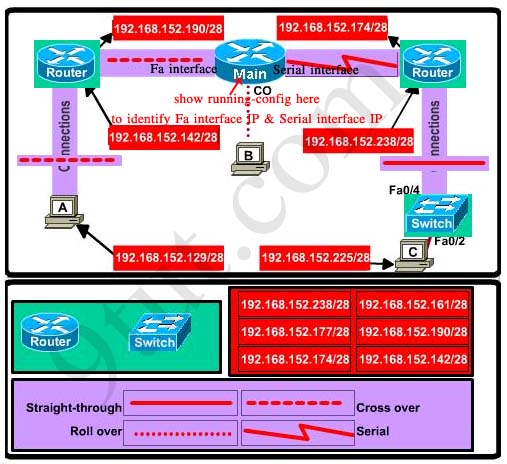
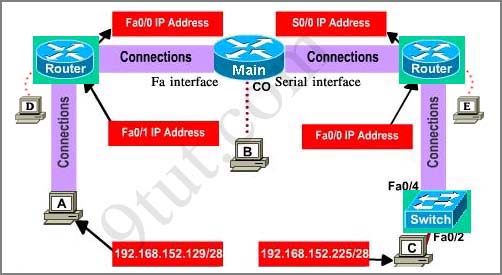
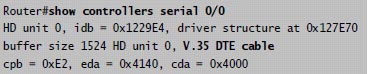
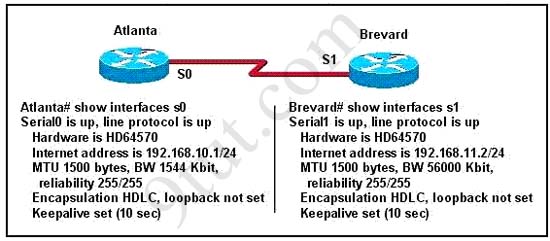
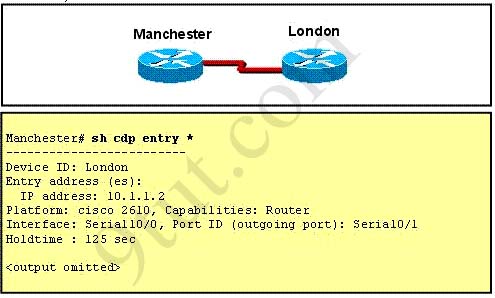
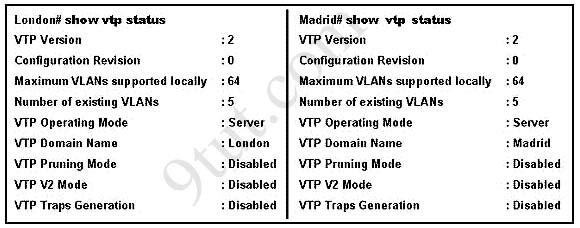
Hotspot Routing Question
Question 1:
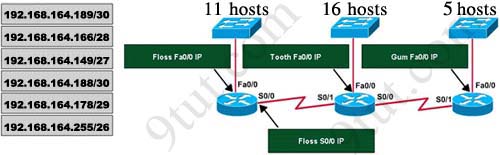
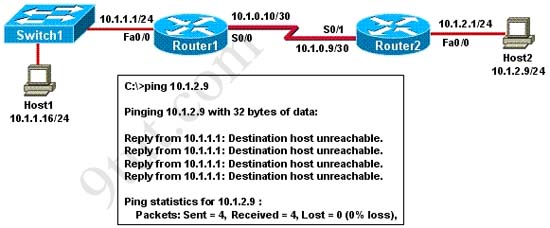
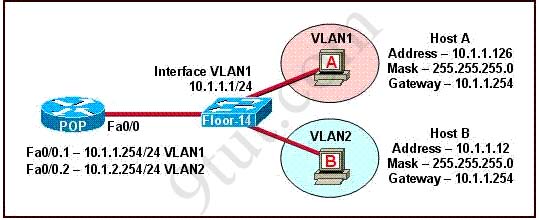
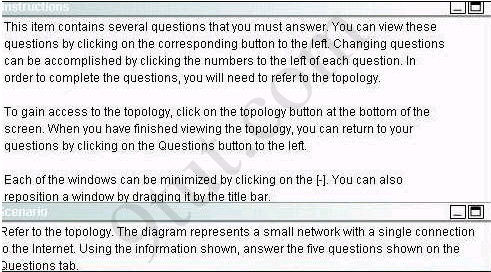
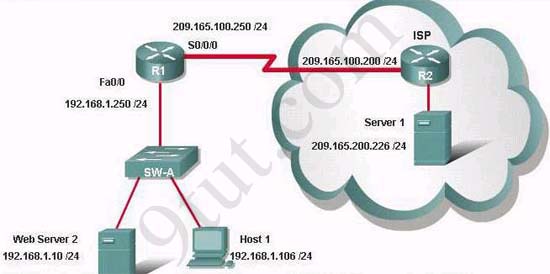
If the router R1 has a packet with a destination address 192.168.1.255, what describes the operation of the network? A - R1 will forward the packet out all interfaces
B - R1 will drop this packet because it is not a valid IP address
C - As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will add 192.168.1.255 to its MAC table
D - R1 will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
E - As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will forward it ti the device assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.255
Answer: B
Question 2:
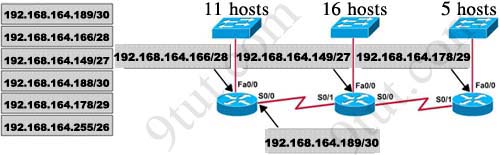
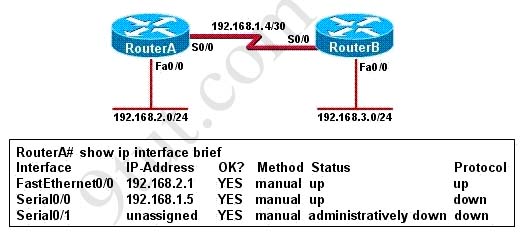
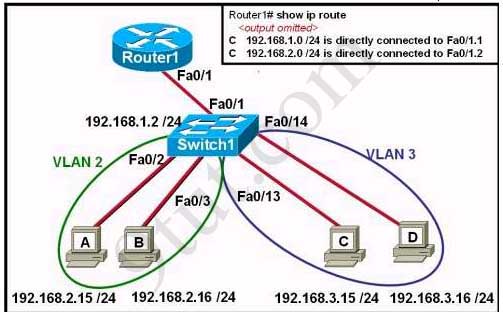
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests to reach the server?A - ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B - ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C - ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D - ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
Answer: A
Quetion 3:
When a packet is sent from Host 1 to Server 1, in how many different frames will the packet be encapsulated as it is sent across the internetwork?A - 0
B - 1
C - 2
D - 3
E - 4
Answer: D
Question 4:
What must be configured on the network in order for users on the Internet to view web pages located on Web Server 2? A - On router R2,configure a default static route to the 192.168.1.0 network
B - On router r2, configure DNS to resolve the URL assigned to Web Server 2 to the 192.168.1.10 address
C - On router R1, configure NAT to translate an address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to 192.168.1.10
D - On router R1, configure DHCP to assign a registered IP address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to Web Server 2
Answer: C
Question 5:
The router address 192.168.1.250 is the default gateway for both the Web Server 2 and Host 1. What is the correct subnet mask for this network? A - 255.255.255.0
B - 255.255.255.192
C - 255.255.255.250
D - 255.255.255.252
Answer: A
Hotspot Frame-relay Question
Question 1:
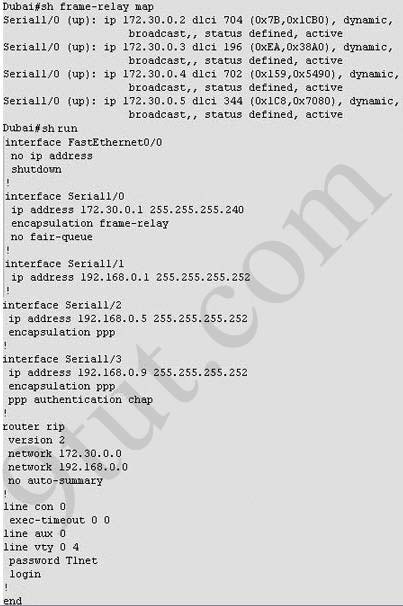
What destination Layer 2 address will be used in the frame header containing a packet for host 172.30.4.4? A - 704
B - 196
C - 702
D - 344
Answer: C
Question 2:
A static map to the S-AMER location is required. Which command should be used to create this map? A - frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 704 broadcast
B - frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 196 broadcast
C - frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 702 broadcast
D - frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 344 broadcast
Answer: B
Question 3:
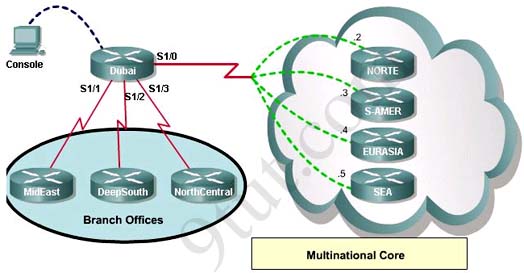
Which connection uses the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers?A - The serial connection to the MidEast branch office
B - The serial connection to the DeepSouth branch office
C - The serial connection to the NorthCentral branch office
D - The serial connection to the Multinational Core
Answer: A
Question 4:
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router? A - No password is required
B - Enable
C - Scr
D - Telnet
E - Console
Answer: D